Learn About Colon Preps
Do not take
information
here as medical advice without consulting a
physician.
What is a Colonoscopy Prep or a Bowel Prep?
Bowel preparation, also known as colon prep,
colonoscopy prep or bowel prep, is the process of removing all
stool, feces and food particles from the colon in order to have a medical or surgical procedure such as a colonoscopy.
It usually entails following an ordered regimen of changing diet accompanied by ingestion of a prescribed combination of drugs prior to the scheduled colonoscopy.
It is important to clean the colon of all stool, food particles and anything else that may be present for two main reasons:
1) It obstructs the ability of the endoscopist to pass the scope through the entire colon.
2) It prevents the endoscopist from seeing small abnormalities in the tissues being inspected.
As you can see in the example above, a well prepared colon is easy to inspect where as an unprepared colon is nearly impossible to inspect even if the surgeon or gastroenterologist is highly trained.
1) Diet : A change in diet on the day preceding the colonoscopy is effective in assisting a Bowel Preparation. Although not sufficient alone, avoiding solid foods and sticking to clear liquids is instrumental in clearing the colon.
2) Polyethylene glycol (PEG) : This is an electrolyte-balanced solution consumed in large amounts the evening before a colonoscopy.
PEG solutions work by pushing a large volume of fluid through the bowel to force out waste. They cause no significant electrolyte shifts, so they are considered safer than OSP solutions (see below). The salty taste may be unpalatable, and the large fluid volume can cause nausea, vomiting, bloating, and cramping. An antinausea drug may be prescribed to help.
Eg. Golytely, Colyte, Nulytely, Trilyte, Halflytely
3) Oral sodium phosphate (OSP) solution : Two small doses of OSP solution diluted in at least 8 ounces of fluid are taken 10 to 12 hours apart. Each dose must be followed by 16 ounces or more of liquid.
OSP draws water into the gut to promote cleansing. It’s as effective as PEG and easier to tolerate, but it can cause dehydration and electrolyte imbalances.
Eg. Fleet Phospho-soda EZ-Prep, Fleet Accu-prep
4) Oral sodium phosphate (OSP) tablets : Twenty tablets are taken the evening before the colonoscopy, 4 at a time with 8 ounces of clear liquid every 15 minutes.
OSP tablets are as effective as liquid OSP or PEG and may be more tolerable. They may cause dehydration and electrolyte imbalances in some people.
Eg. Visicol, Osmoprep
5) Laxatives : Laxatives may be used with lower-volume (2 liters) PEG to result in a well prepared bowel. There are rare reports of ischemic colitis (loss of blood supply to the colon) associated with bisacodyl use.
Eg: Magnesium Citrate, Bisacodyl
1) GoLytely
2) NuLytely
3) Colyte
4) HalfLyte
5) Osmoprep
6) Suprep
7) Moviprep
8) Magnesium Citrate/ Dulcolax
9) Miralax / Dulcolax
The prep medication will usually involve drinking 8oz of liquid every 10-15 minutes until the liquid is completely over. You will experience continuous bowel movements for a few hours until your excretions are completely clear in color. Some prep kits involve drinking less liquid than others and some involve just taking tablets with water.
Common Side Effects of Bowel Prep (present in up to half of all patients)
» Cramping
» Nausea
» Bloating
» Abdominal Pain
» Changes in Taste
» Intestinal Gas
» Dry Mouth
» Increased thirst
» Vomiting
» Sweating
Rare Side Effects of Bowel Prep
(Any of these signs should be reported to your doctor immediately)
» Seizure
» Shortness of Breath
» Facial Redness
» Chest Pain
» Heart Palpitations
» Muscle Weakness
» Acute Renal Failure
Given that many adverse events associated with bowel purgatives may be attributed to dehydration, maintenance of adequate hydration prior to, during and subsequent to colonoscopy may prevent potential dehydration-related complications.
Signs of dehydration include:
» Increased thirst
» Dizziness
» Decreased urine output
» Headache
» Stomach Cramps
» Rapid Heart Beat
» Dry mucous membranes
It usually entails following an ordered regimen of changing diet accompanied by ingestion of a prescribed combination of drugs prior to the scheduled colonoscopy.
Why Is Bowel Preparation needed prior to a Colonoscopy?
A colonoscopy is a procedure where a trained endoscopist will examine the colon with a video scope for abnormalities.It is important to clean the colon of all stool, food particles and anything else that may be present for two main reasons:
1) It obstructs the ability of the endoscopist to pass the scope through the entire colon.
2) It prevents the endoscopist from seeing small abnormalities in the tissues being inspected.
| Colon Preparation Example | |
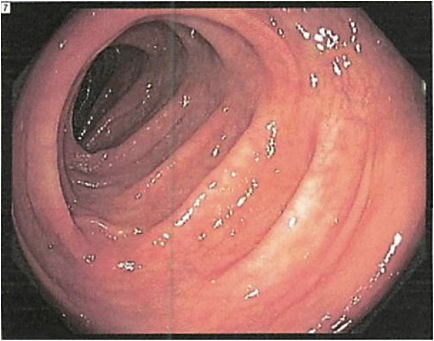 |
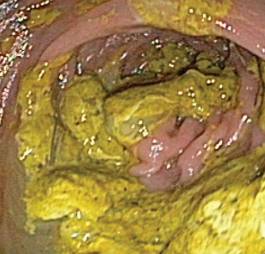 |
| A well prepared colon | A unprepared colon |
As you can see in the example above, a well prepared colon is easy to inspect where as an unprepared colon is nearly impossible to inspect even if the surgeon or gastroenterologist is highly trained.
What are the different types of Colonoscopy Preps?
There are 5 major types of Bowel Preparations. A combination of these will usually be used to reach a well prepared colon.1) Diet : A change in diet on the day preceding the colonoscopy is effective in assisting a Bowel Preparation. Although not sufficient alone, avoiding solid foods and sticking to clear liquids is instrumental in clearing the colon.
2) Polyethylene glycol (PEG) : This is an electrolyte-balanced solution consumed in large amounts the evening before a colonoscopy.
PEG solutions work by pushing a large volume of fluid through the bowel to force out waste. They cause no significant electrolyte shifts, so they are considered safer than OSP solutions (see below). The salty taste may be unpalatable, and the large fluid volume can cause nausea, vomiting, bloating, and cramping. An antinausea drug may be prescribed to help.
Eg. Golytely, Colyte, Nulytely, Trilyte, Halflytely
3) Oral sodium phosphate (OSP) solution : Two small doses of OSP solution diluted in at least 8 ounces of fluid are taken 10 to 12 hours apart. Each dose must be followed by 16 ounces or more of liquid.
OSP draws water into the gut to promote cleansing. It’s as effective as PEG and easier to tolerate, but it can cause dehydration and electrolyte imbalances.
Eg. Fleet Phospho-soda EZ-Prep, Fleet Accu-prep
4) Oral sodium phosphate (OSP) tablets : Twenty tablets are taken the evening before the colonoscopy, 4 at a time with 8 ounces of clear liquid every 15 minutes.
OSP tablets are as effective as liquid OSP or PEG and may be more tolerable. They may cause dehydration and electrolyte imbalances in some people.
Eg. Visicol, Osmoprep
5) Laxatives : Laxatives may be used with lower-volume (2 liters) PEG to result in a well prepared bowel. There are rare reports of ischemic colitis (loss of blood supply to the colon) associated with bisacodyl use.
Eg: Magnesium Citrate, Bisacodyl
What are the common brand name colonoscopy preps?
There are a number of popular colonoscopy preps out there. If instructions are followed properly they will result in a clean colon. The most common bowel preps or colonoscopy prep kits are:1) GoLytely
2) NuLytely
3) Colyte
4) HalfLyte
5) Osmoprep
6) Suprep
7) Moviprep
8) Magnesium Citrate/ Dulcolax
9) Miralax / Dulcolax
What does a colon preparation entail?
A colonoscopy prep will usually involve watching your diet for 2-3 days prior to your colonoscopy followed by taking the prep medication the day prior to your appointment.The prep medication will usually involve drinking 8oz of liquid every 10-15 minutes until the liquid is completely over. You will experience continuous bowel movements for a few hours until your excretions are completely clear in color. Some prep kits involve drinking less liquid than others and some involve just taking tablets with water.
What are the Risks and Side Effects associated with bowel preps?
In general, Colonoscopy Preps are considered to be safe and most patients have no true medical problems. However, some risks and side effects do exists.Common Side Effects of Bowel Prep (present in up to half of all patients)
» Cramping
» Nausea
» Bloating
» Abdominal Pain
» Changes in Taste
» Intestinal Gas
» Dry Mouth
» Increased thirst
» Vomiting
» Sweating
Rare Side Effects of Bowel Prep
(Any of these signs should be reported to your doctor immediately)
» Seizure
» Shortness of Breath
» Facial Redness
» Chest Pain
» Heart Palpitations
» Muscle Weakness
» Acute Renal Failure
Dehydration during Bowel Prep
Dehydration is a particularly important concern when undergoing a colonoscopy prep. During bowel preparation, large amounts of fluid are lost in order to fully evacuate the colon. Replacing these fluids in the form of hydration is an important but commonly overlooked component of the bowel-preparation process.Given that many adverse events associated with bowel purgatives may be attributed to dehydration, maintenance of adequate hydration prior to, during and subsequent to colonoscopy may prevent potential dehydration-related complications.
Signs of dehydration include:
» Increased thirst
» Dizziness
» Decreased urine output
» Headache
» Stomach Cramps
» Rapid Heart Beat
» Dry mucous membranes


